
The V Programming Language
[vlang.io](https://vlang.io) | [Docs](https://github.com/vlang/v/blob/master/doc/docs.md) | [Changelog](https://github.com/vlang/v/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) | [Speed](https://fast.vlang.io/) | [Contributing & compiler design](https://github.com/vlang/v/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)
[![Sponsor][SponsorBadge]][SponsorUrl]
[![Patreon][PatreonBadge]][PatreonUrl]
[![Discord][DiscordBadge]][DiscordUrl]
[![Twitter][TwitterBadge]][TwitterUrl]
[![Modules][ModulesBadge]][ModulesUrl]
## Key Features of V
- Simplicity: the language can be learned over the course of a weekend
- Fast compilation: ≈110k loc/s with a Clang backend,
≈500k loc/s with native and tcc backends *(Intel i5-7500, SSD, no
optimization)* ([demo video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pvP6wmcl_Sc))
- Easy to develop: V compiles itself in less than a second
- Performance: as fast as C (V's main backend compiles to human-readable C)
- Safety: no null, no globals, no undefined behavior (wip), immutability by default
- C to V translation ([Translating DOOM demo video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6oXrz3oRoEg))
- Hot code reloading
- [Flexible memory management](https://vlang.io/#memory). GC by default, manual via `v -gc none`,
arena allocation via `v -prealloc`, autofree via `v -autofree`
([autofree demo video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gmB8ea8uLsM)).
- [Cross-platform UI library](https://github.com/vlang/ui)
- Built-in graphics library
- Easy cross-compilation
- REPL
- [Built-in ORM](https://github.com/vlang/v/blob/master/doc/docs.md#orm)
- [Built-in web framework](https://github.com/vlang/v/blob/master/vlib/vweb/README.md)
- C and JavaScript backends
- Great for writing low-level software ([Vinix OS](https://github.com/vlang/vinix))
## Stability guarantee and future changes
Despite being at an early development stage, the V language is relatively stable and has
backwards compatibility guarantee, meaning that the code you write today is guaranteed
to work a month, a year, or five years from now.
There still may be minor syntax changes before the 1.0 release, but they will be handled
automatically via `vfmt`, as has been done in the past.
The V core APIs (primarily the `os` module) will still have minor changes until
they are stabilized in V 1.0. Of course the APIs will grow after that, but without breaking
existing code.
Unlike many other languages, V is not going to be always changing, with new features
being introduced and old features modified. It is always going to be a small and simple
language, very similar to the way it is right now.
## Installing V from source
--> **_(this is the preferred method)_**
### Linux, macOS, Windows, *BSD, Solaris, WSL, etc.
Usually, installing V is quite simple if you have an environment that already has a
functional `git` installation.
To get started, simply try to execute the following in your terminal/shell:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/vlang/v
cd v
make
# HINT: Using Windows? run make.bat in a cmd shell, or ./make.bat in PowerShell
```
That should be it and you should find your V executable at `[path to V repo]/v`.
`[path to V repo]` can be anywhere.
(As in the hint above, on Windows `make` means running `make.bat`.)
Now you can try `./v run examples/hello_world.v` (or `v run examples/hello_world.v` in cmd shell).
* *Trouble? Please see the note above and link to
[Installation Issues](https://github.com/vlang/v/discussions/categories/installation-issues)
for help.*
V is constantly being updated. To update V, simply run:
```bash
v up
```
> **Note**
> If you run into any trouble, or you have a different operating
> system or Linux distribution that doesn't install or work immediately, please see
> [Installation Issues](https://github.com/vlang/v/discussions/categories/installation-issues)
> and search for your OS and problem.
>
> If you can't find your problem, please add it to an existing discussion if one exists for
> your OS, or create a new one if a main discussion doesn't yet exist for your OS.
### C compiler
The [Tiny C Compiler (tcc)](https://repo.or.cz/w/tinycc.git) is downloaded for you by `make` if
there is a compatible version for your system, and installed under the V `thirdparty` directory.
This compiler is very fast, but does almost no optimizations. It is best for development builds.
For production builds (using the `-prod` option to V), it's recommended to use clang, gcc, or
Microsoft Visual C++. If you are doing development, you most likely already have one of those
installed.
Otherwise, follow these instructions:
- [Installing a C compiler on Linux and macOS](https://github.com/vlang/v/wiki/Installing-a-C-compiler-on-Linux-and-macOS)
- [Installing a C compiler on Windows](https://github.com/vlang/v/wiki/Installing-a-C-compiler-on-Windows)
### Symlinking
> **Note**
> It is *highly recommended*, that you put V on your PATH. That saves
> you the effort to type in the full path to your v executable every time.
> V provides a convenience `v symlink` command to do that more easily.
On Unix systems, it creates a `/usr/local/bin/v` symlink to your
executable. To do that, run:
```bash
sudo ./v symlink
```
On Windows, start a new shell with administrative privileges, for example by pressing the
Windows Key, then type `cmd.exe`, right-click on its menu entry, and choose `Run as
administrator`. In the new administrative shell, cd to the path where you have compiled V, then
type:
```bat
v symlink
```
(or `./v symlink` in PowerShell)
That will make V available everywhere, by adding it to your PATH. Please restart your
shell/editor after that, so that it can pick up the new PATH variable.
> **Note**
> There is no need to run `v symlink` more than once - v will still be available, even after
> `v up`, restarts, and so on. You only need to run it again if you decide to move the V repo
> folder somewhere else.
### Void Linux
Expand Void Linux instructions
```bash
# xbps-install -Su base-devel
# xbps-install libatomic-devel
$ git clone https://github.com/vlang/v
$ cd v
$ make
```
Expand Docker instructions
```bash
git clone https://github.com/vlang/v
cd v
docker build -t vlang .
docker run --rm -it vlang:latest
```
### Docker with Alpine/musl
```bash
git clone https://github.com/vlang/v
cd v
docker build -t vlang --file=Dockerfile.alpine .
docker run --rm -it vlang:latest
```
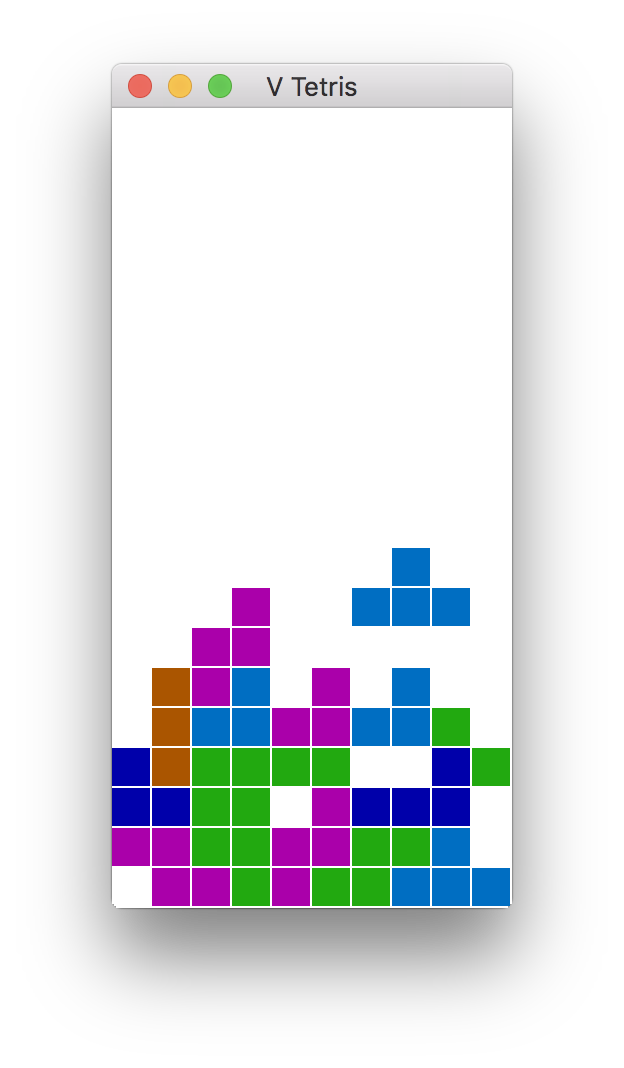 In order to build Tetris or 2048 (or anything else using `sokol` or `gg` graphics modules),
you will need additional development libraries for your system.
| System | Installation method |
|---------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libxi-dev libxcursor-dev libgl-dev` |
| Fedora/RH/CentOS | `sudo dnf install libXcursor-devel libXi-devel libX11-devel libglvnd-devel` |
| NixOS | add `xorg.libX11.dev xorg.libXcursor.dev xorg.libXi.dev libGL.dev` to `environment.systemPackages` |
## V net.http, net.websocket, `v install`
The net.http module, the net.websocket module, and the `v install` command may all use SSL.
V comes with a version of mbedtls, which should work on all systems. If you find a need to
use OpenSSL instead, you will need to make sure that it is installed on your system, then
use the `-d use_openssl` switch when you compile.
To install OpenSSL on non-Windows systems:
| System | Installation command |
|---------------------|----------------------------------|
| macOS | `brew install openssl` |
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libssl-dev` |
| Arch/Manjaro | openssl is installed by default |
| Fedora/CentOS/RH | `sudo dnf install openssl-devel` |
On Windows, OpenSSL is simply hard to get working correctly. The instructions
[here](https://tecadmin.net/install-openssl-on-windows/) may (or may not) help.
## V sync
V's `sync` module and channel implementation uses libatomic.
It is most likely already installed on your system, but if not,
you can install it, by doing the following:
| System | Installation command |
|---------------------|-------------------------------------|
| macOS | already installed |
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libatomic1` |
| Fedora/CentOS/RH | `sudo dnf install libatomic-static` |
## V UI
In order to build Tetris or 2048 (or anything else using `sokol` or `gg` graphics modules),
you will need additional development libraries for your system.
| System | Installation method |
|---------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libxi-dev libxcursor-dev libgl-dev` |
| Fedora/RH/CentOS | `sudo dnf install libXcursor-devel libXi-devel libX11-devel libglvnd-devel` |
| NixOS | add `xorg.libX11.dev xorg.libXcursor.dev xorg.libXi.dev libGL.dev` to `environment.systemPackages` |
## V net.http, net.websocket, `v install`
The net.http module, the net.websocket module, and the `v install` command may all use SSL.
V comes with a version of mbedtls, which should work on all systems. If you find a need to
use OpenSSL instead, you will need to make sure that it is installed on your system, then
use the `-d use_openssl` switch when you compile.
To install OpenSSL on non-Windows systems:
| System | Installation command |
|---------------------|----------------------------------|
| macOS | `brew install openssl` |
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libssl-dev` |
| Arch/Manjaro | openssl is installed by default |
| Fedora/CentOS/RH | `sudo dnf install openssl-devel` |
On Windows, OpenSSL is simply hard to get working correctly. The instructions
[here](https://tecadmin.net/install-openssl-on-windows/) may (or may not) help.
## V sync
V's `sync` module and channel implementation uses libatomic.
It is most likely already installed on your system, but if not,
you can install it, by doing the following:
| System | Installation command |
|---------------------|-------------------------------------|
| macOS | already installed |
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libatomic1` |
| Fedora/CentOS/RH | `sudo dnf install libatomic-static` |
## V UI
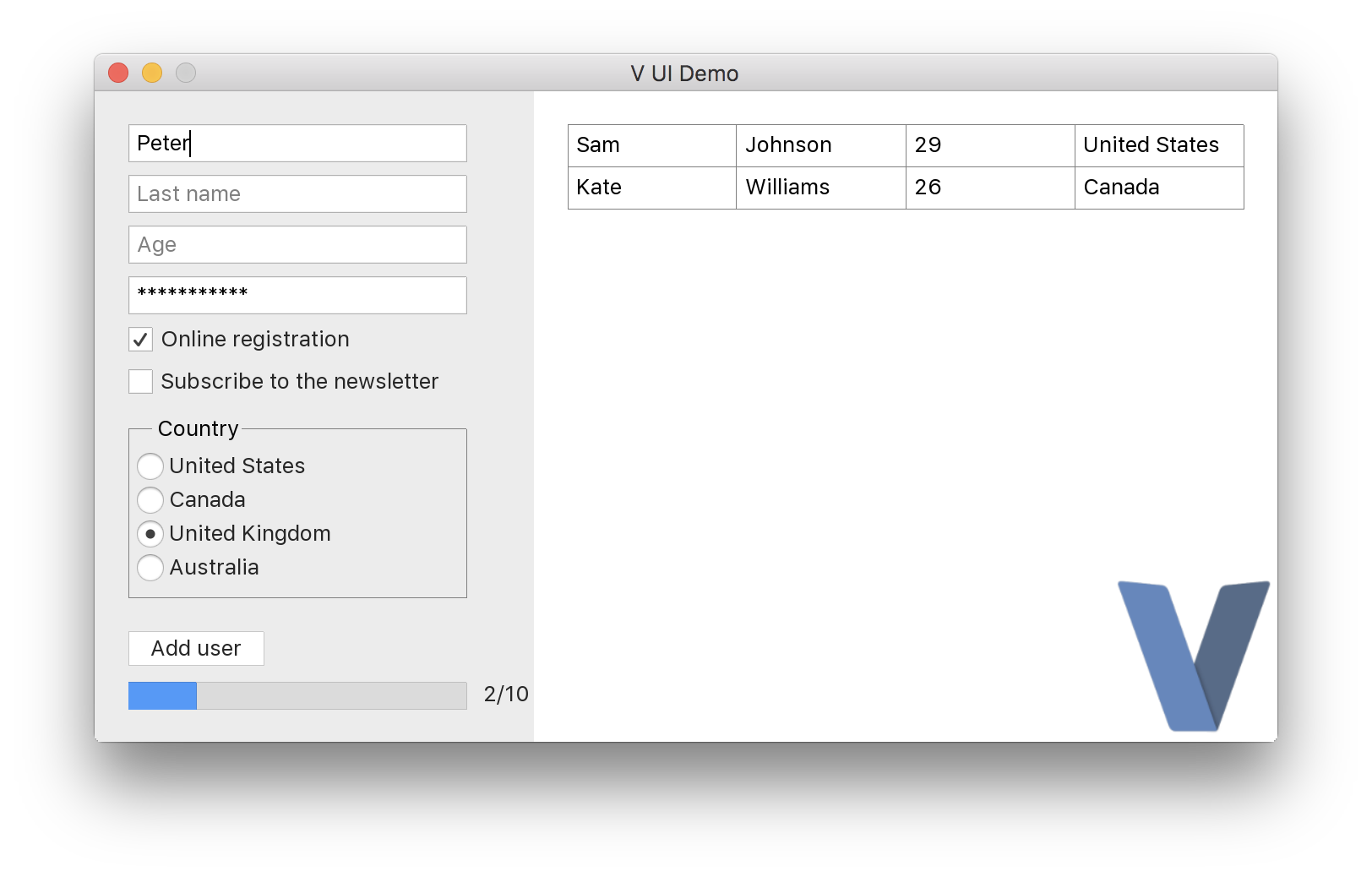 https://github.com/vlang/ui
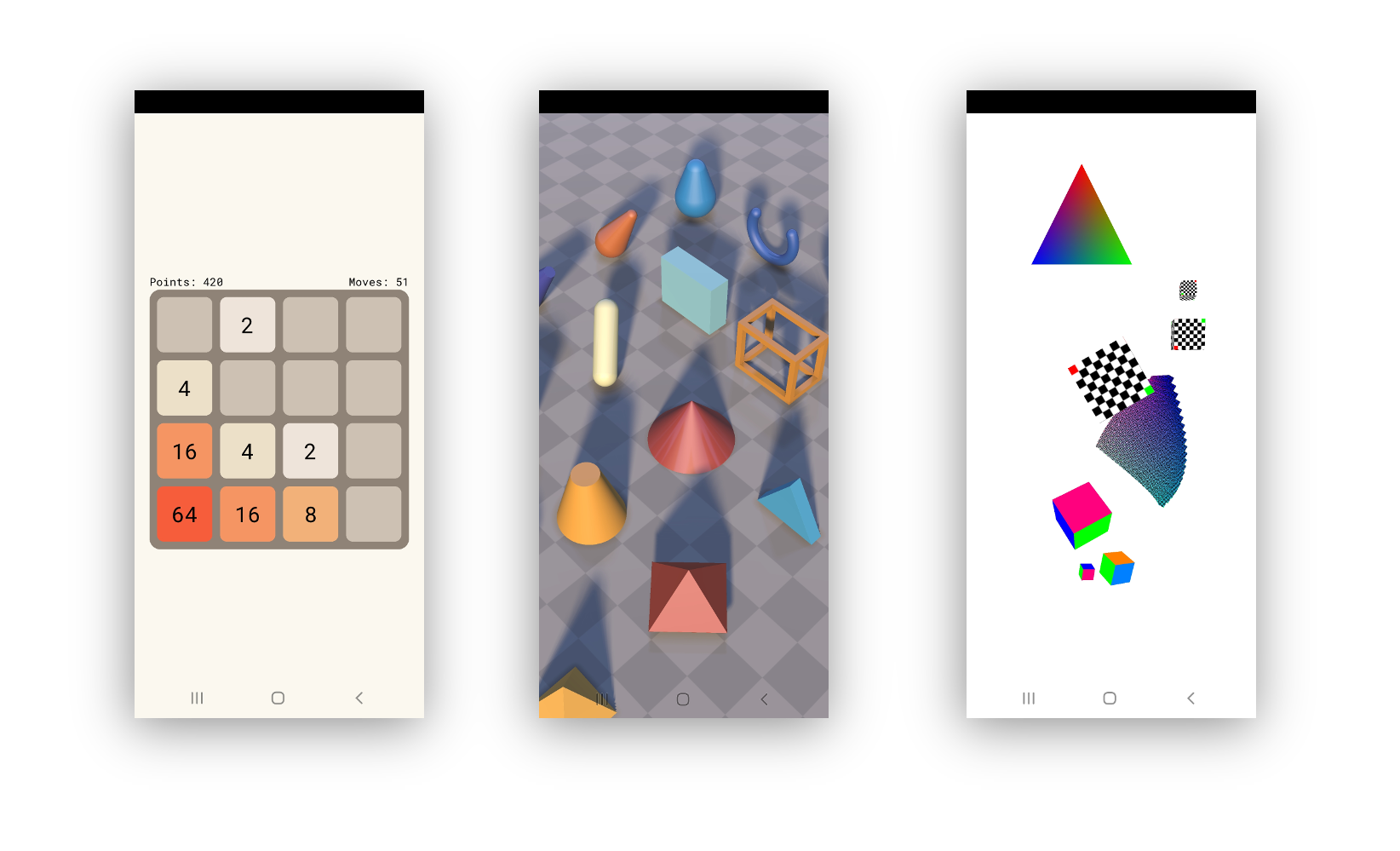
## Android graphical apps
With V's `vab` tool, building V UI and graphical apps for Android can become as easy as:
```
./vab /path/to/v/examples/2048
```
[https://github.com/vlang/vab](https://github.com/vlang/vab).
https://github.com/vlang/ui
## Android graphical apps
With V's `vab` tool, building V UI and graphical apps for Android can become as easy as:
```
./vab /path/to/v/examples/2048
```
[https://github.com/vlang/vab](https://github.com/vlang/vab).
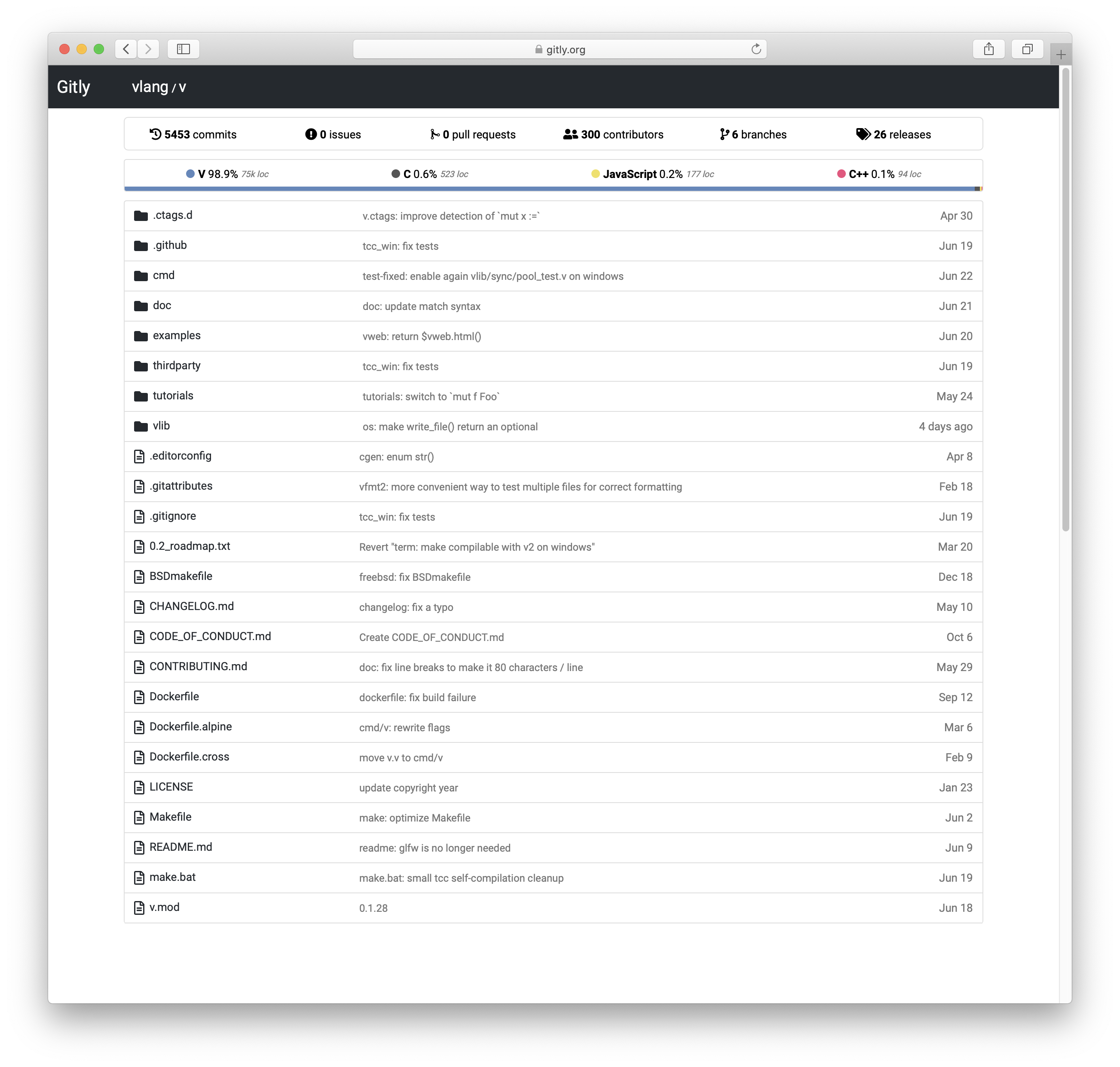
 ## Developing web applications
Check out the
[Building a simple web blog](https://github.com/vlang/v/blob/master/tutorials/building_a_simple_web_blog_with_vweb/README.md)
tutorial and Gitly, a light and fast alternative to GitHub/GitLab:
https://github.com/vlang/gitly
## Developing web applications
Check out the
[Building a simple web blog](https://github.com/vlang/v/blob/master/tutorials/building_a_simple_web_blog_with_vweb/README.md)
tutorial and Gitly, a light and fast alternative to GitHub/GitLab:
https://github.com/vlang/gitly
 ## Vinix, an OS/kernel written in V
V is great for writing low-level software like drivers and kernels.
Vinix is an OS/kernel that already runs bash, GCC, V, and nano.
https://github.com/vlang/vinix
## Vinix, an OS/kernel written in V
V is great for writing low-level software like drivers and kernels.
Vinix is an OS/kernel that already runs bash, GCC, V, and nano.
https://github.com/vlang/vinix

 ## Acknowledgement
V thanks Fabrice Bellard for his original work on the
[TCC - Tiny C Compiler](https://bellard.org/tcc/).
Note the TCC website is old; the current TCC repository can be found
[here](https://repo.or.cz/w/tinycc.git).
V utilizes pre-built TCC binaries located at
[https://github.com/vlang/tccbin/](https://github.com/vlang/tccbin/).
## Troubleshooting
Please see the
[Troubleshooting](https://github.com/vlang/v/wiki/Troubleshooting)
section on our
[wiki page](https://github.com/vlang/v/wiki).
[WorkflowBadge]: https://github.com/vlang/v/workflows/CI/badge.svg
[DiscordBadge]: https://img.shields.io/discord/592103645835821068?label=Discord&logo=discord&logoColor=white
[PatreonBadge]: https://img.shields.io/endpoint.svg?url=https%3A%2F%2Fshieldsio-patreon.vercel.app%2Fapi%3Fusername%3Dvlang%26type%3Dpatrons&style=flat
[SponsorBadge]: https://camo.githubusercontent.com/da8bc40db5ed31e4b12660245535b5db67aa03ce/68747470733a2f2f696d672e736869656c64732e696f2f7374617469632f76313f6c6162656c3d53706f6e736f72266d6573736167653d254532253944254134266c6f676f3d476974487562
[TwitterBadge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/follow-%40v_language-1DA1F2?logo=twitter&style=flat&logoColor=white&color=1da1f2
[ModulesBadge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/modules-reference-027d9c?logo=v&logoColor=white&logoWidth=10
[WorkflowUrl]: https://github.com/vlang/v/commits/master
[DiscordUrl]: https://discord.gg/vlang
[PatreonUrl]: https://patreon.com/vlang
[SponsorUrl]: https://github.com/sponsors/medvednikov
[TwitterUrl]: https://twitter.com/v_language
[ModulesUrl]: https://modules.vlang.io
## Acknowledgement
V thanks Fabrice Bellard for his original work on the
[TCC - Tiny C Compiler](https://bellard.org/tcc/).
Note the TCC website is old; the current TCC repository can be found
[here](https://repo.or.cz/w/tinycc.git).
V utilizes pre-built TCC binaries located at
[https://github.com/vlang/tccbin/](https://github.com/vlang/tccbin/).
## Troubleshooting
Please see the
[Troubleshooting](https://github.com/vlang/v/wiki/Troubleshooting)
section on our
[wiki page](https://github.com/vlang/v/wiki).
[WorkflowBadge]: https://github.com/vlang/v/workflows/CI/badge.svg
[DiscordBadge]: https://img.shields.io/discord/592103645835821068?label=Discord&logo=discord&logoColor=white
[PatreonBadge]: https://img.shields.io/endpoint.svg?url=https%3A%2F%2Fshieldsio-patreon.vercel.app%2Fapi%3Fusername%3Dvlang%26type%3Dpatrons&style=flat
[SponsorBadge]: https://camo.githubusercontent.com/da8bc40db5ed31e4b12660245535b5db67aa03ce/68747470733a2f2f696d672e736869656c64732e696f2f7374617469632f76313f6c6162656c3d53706f6e736f72266d6573736167653d254532253944254134266c6f676f3d476974487562
[TwitterBadge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/follow-%40v_language-1DA1F2?logo=twitter&style=flat&logoColor=white&color=1da1f2
[ModulesBadge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/modules-reference-027d9c?logo=v&logoColor=white&logoWidth=10
[WorkflowUrl]: https://github.com/vlang/v/commits/master
[DiscordUrl]: https://discord.gg/vlang
[PatreonUrl]: https://patreon.com/vlang
[SponsorUrl]: https://github.com/sponsors/medvednikov
[TwitterUrl]: https://twitter.com/v_language
[ModulesUrl]: https://modules.vlang.io In order to build Tetris or 2048 (or anything else using `sokol` or `gg` graphics modules),
you will need additional development libraries for your system.
| System | Installation method |
|---------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libxi-dev libxcursor-dev libgl-dev` |
| Fedora/RH/CentOS | `sudo dnf install libXcursor-devel libXi-devel libX11-devel libglvnd-devel` |
| NixOS | add `xorg.libX11.dev xorg.libXcursor.dev xorg.libXi.dev libGL.dev` to `environment.systemPackages` |
## V net.http, net.websocket, `v install`
The net.http module, the net.websocket module, and the `v install` command may all use SSL.
V comes with a version of mbedtls, which should work on all systems. If you find a need to
use OpenSSL instead, you will need to make sure that it is installed on your system, then
use the `-d use_openssl` switch when you compile.
To install OpenSSL on non-Windows systems:
| System | Installation command |
|---------------------|----------------------------------|
| macOS | `brew install openssl` |
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libssl-dev` |
| Arch/Manjaro | openssl is installed by default |
| Fedora/CentOS/RH | `sudo dnf install openssl-devel` |
On Windows, OpenSSL is simply hard to get working correctly. The instructions
[here](https://tecadmin.net/install-openssl-on-windows/) may (or may not) help.
## V sync
V's `sync` module and channel implementation uses libatomic.
It is most likely already installed on your system, but if not,
you can install it, by doing the following:
| System | Installation command |
|---------------------|-------------------------------------|
| macOS | already installed |
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libatomic1` |
| Fedora/CentOS/RH | `sudo dnf install libatomic-static` |
## V UI
In order to build Tetris or 2048 (or anything else using `sokol` or `gg` graphics modules),
you will need additional development libraries for your system.
| System | Installation method |
|---------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libxi-dev libxcursor-dev libgl-dev` |
| Fedora/RH/CentOS | `sudo dnf install libXcursor-devel libXi-devel libX11-devel libglvnd-devel` |
| NixOS | add `xorg.libX11.dev xorg.libXcursor.dev xorg.libXi.dev libGL.dev` to `environment.systemPackages` |
## V net.http, net.websocket, `v install`
The net.http module, the net.websocket module, and the `v install` command may all use SSL.
V comes with a version of mbedtls, which should work on all systems. If you find a need to
use OpenSSL instead, you will need to make sure that it is installed on your system, then
use the `-d use_openssl` switch when you compile.
To install OpenSSL on non-Windows systems:
| System | Installation command |
|---------------------|----------------------------------|
| macOS | `brew install openssl` |
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libssl-dev` |
| Arch/Manjaro | openssl is installed by default |
| Fedora/CentOS/RH | `sudo dnf install openssl-devel` |
On Windows, OpenSSL is simply hard to get working correctly. The instructions
[here](https://tecadmin.net/install-openssl-on-windows/) may (or may not) help.
## V sync
V's `sync` module and channel implementation uses libatomic.
It is most likely already installed on your system, but if not,
you can install it, by doing the following:
| System | Installation command |
|---------------------|-------------------------------------|
| macOS | already installed |
| Debian/Ubuntu based | `sudo apt install libatomic1` |
| Fedora/CentOS/RH | `sudo dnf install libatomic-static` |
## V UI
 https://github.com/vlang/ui
## Android graphical apps
With V's `vab` tool, building V UI and graphical apps for Android can become as easy as:
```
./vab /path/to/v/examples/2048
```
[https://github.com/vlang/vab](https://github.com/vlang/vab).
https://github.com/vlang/ui
## Android graphical apps
With V's `vab` tool, building V UI and graphical apps for Android can become as easy as:
```
./vab /path/to/v/examples/2048
```
[https://github.com/vlang/vab](https://github.com/vlang/vab).
 ## Developing web applications
Check out the
[Building a simple web blog](https://github.com/vlang/v/blob/master/tutorials/building_a_simple_web_blog_with_vweb/README.md)
tutorial and Gitly, a light and fast alternative to GitHub/GitLab:
https://github.com/vlang/gitly
## Developing web applications
Check out the
[Building a simple web blog](https://github.com/vlang/v/blob/master/tutorials/building_a_simple_web_blog_with_vweb/README.md)
tutorial and Gitly, a light and fast alternative to GitHub/GitLab:
https://github.com/vlang/gitly
 ## Vinix, an OS/kernel written in V
V is great for writing low-level software like drivers and kernels.
Vinix is an OS/kernel that already runs bash, GCC, V, and nano.
https://github.com/vlang/vinix
## Vinix, an OS/kernel written in V
V is great for writing low-level software like drivers and kernels.
Vinix is an OS/kernel that already runs bash, GCC, V, and nano.
https://github.com/vlang/vinix

 ## Acknowledgement
V thanks Fabrice Bellard for his original work on the
[TCC - Tiny C Compiler](https://bellard.org/tcc/).
Note the TCC website is old; the current TCC repository can be found
[here](https://repo.or.cz/w/tinycc.git).
V utilizes pre-built TCC binaries located at
[https://github.com/vlang/tccbin/](https://github.com/vlang/tccbin/).
## Troubleshooting
Please see the
[Troubleshooting](https://github.com/vlang/v/wiki/Troubleshooting)
section on our
[wiki page](https://github.com/vlang/v/wiki).
[WorkflowBadge]: https://github.com/vlang/v/workflows/CI/badge.svg
[DiscordBadge]: https://img.shields.io/discord/592103645835821068?label=Discord&logo=discord&logoColor=white
[PatreonBadge]: https://img.shields.io/endpoint.svg?url=https%3A%2F%2Fshieldsio-patreon.vercel.app%2Fapi%3Fusername%3Dvlang%26type%3Dpatrons&style=flat
[SponsorBadge]: https://camo.githubusercontent.com/da8bc40db5ed31e4b12660245535b5db67aa03ce/68747470733a2f2f696d672e736869656c64732e696f2f7374617469632f76313f6c6162656c3d53706f6e736f72266d6573736167653d254532253944254134266c6f676f3d476974487562
[TwitterBadge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/follow-%40v_language-1DA1F2?logo=twitter&style=flat&logoColor=white&color=1da1f2
[ModulesBadge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/modules-reference-027d9c?logo=v&logoColor=white&logoWidth=10
[WorkflowUrl]: https://github.com/vlang/v/commits/master
[DiscordUrl]: https://discord.gg/vlang
[PatreonUrl]: https://patreon.com/vlang
[SponsorUrl]: https://github.com/sponsors/medvednikov
[TwitterUrl]: https://twitter.com/v_language
[ModulesUrl]: https://modules.vlang.io
## Acknowledgement
V thanks Fabrice Bellard for his original work on the
[TCC - Tiny C Compiler](https://bellard.org/tcc/).
Note the TCC website is old; the current TCC repository can be found
[here](https://repo.or.cz/w/tinycc.git).
V utilizes pre-built TCC binaries located at
[https://github.com/vlang/tccbin/](https://github.com/vlang/tccbin/).
## Troubleshooting
Please see the
[Troubleshooting](https://github.com/vlang/v/wiki/Troubleshooting)
section on our
[wiki page](https://github.com/vlang/v/wiki).
[WorkflowBadge]: https://github.com/vlang/v/workflows/CI/badge.svg
[DiscordBadge]: https://img.shields.io/discord/592103645835821068?label=Discord&logo=discord&logoColor=white
[PatreonBadge]: https://img.shields.io/endpoint.svg?url=https%3A%2F%2Fshieldsio-patreon.vercel.app%2Fapi%3Fusername%3Dvlang%26type%3Dpatrons&style=flat
[SponsorBadge]: https://camo.githubusercontent.com/da8bc40db5ed31e4b12660245535b5db67aa03ce/68747470733a2f2f696d672e736869656c64732e696f2f7374617469632f76313f6c6162656c3d53706f6e736f72266d6573736167653d254532253944254134266c6f676f3d476974487562
[TwitterBadge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/follow-%40v_language-1DA1F2?logo=twitter&style=flat&logoColor=white&color=1da1f2
[ModulesBadge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/modules-reference-027d9c?logo=v&logoColor=white&logoWidth=10
[WorkflowUrl]: https://github.com/vlang/v/commits/master
[DiscordUrl]: https://discord.gg/vlang
[PatreonUrl]: https://patreon.com/vlang
[SponsorUrl]: https://github.com/sponsors/medvednikov
[TwitterUrl]: https://twitter.com/v_language
[ModulesUrl]: https://modules.vlang.io